Casual Tips About How To Detect Pituitary Tumor
 Detecting a pituitary tumor is a multi-step process that combines recognizing clinical symptoms with specialized diagnostic tests. Here's a comprehensive, step-by-step guide illustrating how medical professionals identify pituitary tumors in real-life scenarios:
Detecting a pituitary tumor is a multi-step process that combines recognizing clinical symptoms with specialized diagnostic tests. Here's a comprehensive, step-by-step guide illustrating how medical professionals identify pituitary tumors in real-life scenarios:
1. Recognizing Clinical Symptoms
a. Hormonal Imbalances:- Excess Hormone Production: Depending on the type of pituitary tumor (functional), it may secrete excess hormones, leading to conditions such as:
- Prolactinomas: Excess prolactin causing menstrual disturbances in women and decreased libido in men.
- Growth Hormone-Secreting Tumors: Leading to acromegaly in adults or gigantism in children.
- ACTH-Secreting Tumors: Causing Cushing's disease with symptoms like weight gain, high blood pressure, and osteoporosis.
- Hormone Deficiency: Non-functional tumors can compress normal pituitary tissue, reducing hormone production and causing symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and decreased libido.
- Bitemporal Hemianopsia: Loss of peripheral vision in both eyes due to the tumor pressing on the optic chiasm.
- Other Visual Field Defects: Depending on tumor size and location.
- Headaches: Often persistent and worsening over time.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Resulting from increased intracranial pressure.
2. Comprehensive Medical History and Physical Examination
a. Medical History:- Symptom Inquiry: Detailed questioning about the onset, duration, and nature of symptoms.
- Family History: Assessing for any hereditary conditions related to endocrine disorders.
- Neurological Assessment: Checking for visual field deficits and other neurological signs.
- Signs of Hormonal Imbalance: Such as changes in skin texture, body habitus, or secondary sexual characteristics.
3. Laboratory Tests for Hormonal Evaluation
a. Baseline Hormone Levels:- Pituitary Hormones: Measuring levels of prolactin, growth hormone (GH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and others.
- Target Gland Hormones: Assessing cortisol, thyroid hormones (T3 and T4), sex hormones (estrogen, testosterone), and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1).
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test: To assess growth hormone suppression.
- Dexamethasone Suppression Test: To evaluate cortisol production.
- TRH Stimulation Test: To assess TSH and prolactin response.
4. Imaging Studies
a. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):- Preferred Modality: MRI provides high-resolution images of the pituitary gland and surrounding structures.
- Contrast Enhancement: Helps in delineating the tumor from normal tissue.
- Alternative Option: Used if MRI is contraindicated (e.g., in patients with certain implants).
- Detail on Bone Structures: Useful for assessing any bony changes in the sella turcica.
5. Visual Field Testing
a. Perimetry:- Automated Visual Field Tests: Detects specific patterns of vision loss associated with pituitary tumors.
- Frequency of Testing: May be repeated to monitor changes over time.
6. Biopsy (Rarely Required)
- When Necessary: Typically not needed unless there’s suspicion of a malignant tumor.
- Procedure: Performed via a transsphenoidal approach, where a surgeon accesses the pituitary gland through the nasal passages.
7. Multidisciplinary Consultation
a. Endocrinologist:- Role: Manages hormonal imbalances and oversees medical therapy.
- Role: Assesses the need for surgical intervention, especially in cases of large tumors causing significant compression.
- Role: Evaluates and manages visual field defects.
8. Treatment Planning and Follow-Up
a. Treatment Options:- Medication: For hormone-secreting tumors (e.g., dopamine agonists for prolactinomas).
- Surgery: Often the first-line treatment for large tumors or those causing significant symptoms.
- Radiation Therapy: Used when surgery isn’t feasible or as an adjunct treatment.
- Imaging: Periodic MRI scans to monitor tumor size.
- Hormonal Levels: Routine blood tests to ensure hormonal balance is maintained.
Real-Life Application Example
Case Study: A 45-year-old woman presents with irregular menstrual cycles, unexplained weight gain, and headaches. During the physical examination, she exhibits signs of hypothyroidism. Based on her symptoms, the healthcare provider suspects a pituitary disorder. Step-by-Step Detection:- Symptom Recognition: Menstrual irregularities and weight gain suggest hormonal imbalance.
- Medical History & Examination: Reveals possible signs of decreased thyroid function.
- Laboratory Tests: Elevated prolactin levels and low thyroid hormones indicate pituitary dysfunction.
- Imaging: An MRI is ordered, revealing a macroadenoma (a large pituitary tumor).
- Visual Field Testing: Shows mild bitemporal hemianopsia, confirming the tumor's effect on the optic chiasm.
- Multidisciplinary Consultation: An endocrinologist and neurosurgeon evaluate the case.
- Treatment Plan: The patient undergoes transsphenoidal surgery to remove the tumor, followed by hormone replacement therapy as needed.
- Follow-Up: Regular MRI scans and blood tests ensure the tumor does not recur and hormonal levels remain stable.
Key Takeaways
- Early Detection is Crucial: Timely identification of pituitary tumors can prevent complications related to hormonal imbalances and neurological deficits.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Effective management often involves collaboration among various specialists.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing assessment ensures successful treatment outcomes and manages any recurrence promptly.
Pituitary Tumor Signs And Symptoms Robert Louis, Md

How I Discovered Have A Pituitary Tumor By Ayra M.c. Medium
Pituitary Tumor 10 Symptoms Of A

Longterm Efficacy Of Temozolomide Not Seen For Pituitary Tumors
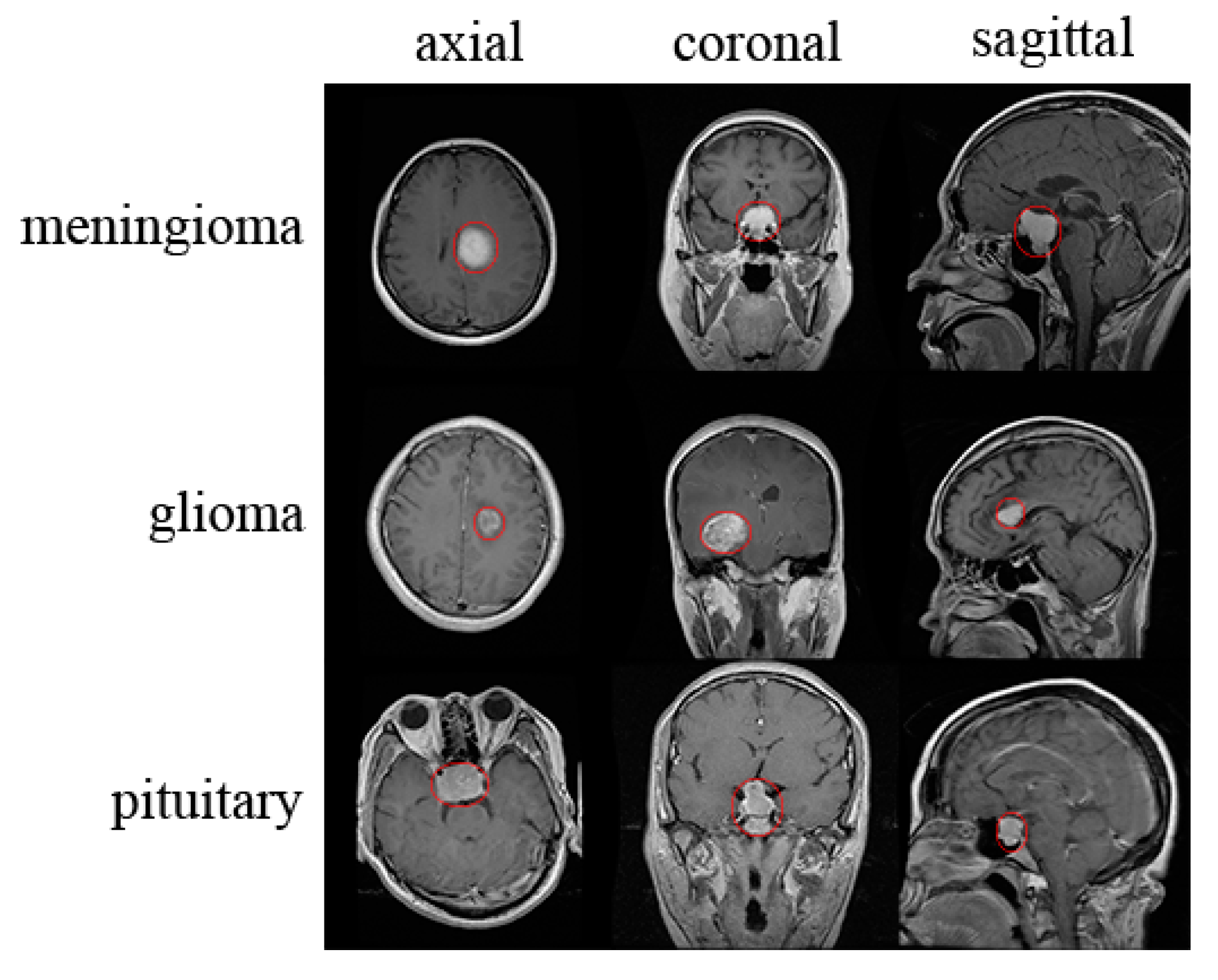
Github Ansamz/mribraintumordetector Trying Different Image

Comments
Post a Comment